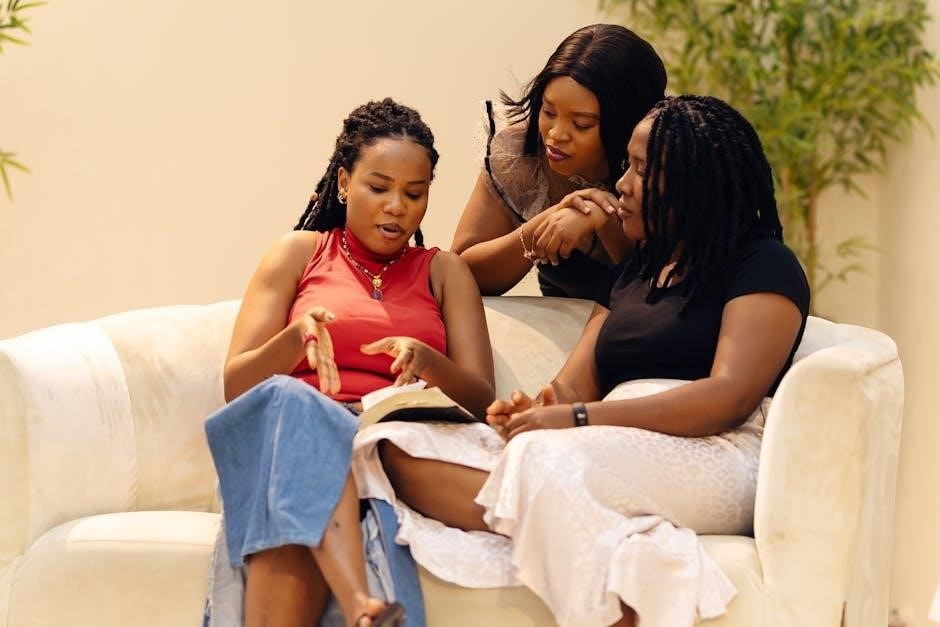
The concept of love in the Bible is profound, encompassing various forms that guide us in understanding divine and human connections. This section explores these transformative principles, enriching faith and relationships.
Overview and Importance of Biblical Love
Biblical love is a foundational concept that shapes relationships, faith, and personal growth. It transcends human emotions, reflecting God’s divine nature and His plan for humanity; Love in the Bible is not merely an emotion but a choice and commitment rooted in faith. The seven types of love—eros, storge, philia, agape, ludus, pragma, and philautia—highlight diverse expressions of love, each with unique significance. Understanding these types provides insight into God’s design for love in all aspects of life, from romantic relationships to self-love. Biblical love emphasizes unconditional care, forgiveness, and selflessness, serving as a moral and spiritual guide. It calls believers to mirror God’s love in their interactions, fostering unity, compassion, and grace. By studying these principles, individuals can deepen their faith, nurture meaningful connections, and align their lives with God’s will.
The Seven Types of Love in the Bible
The Bible explores seven distinct forms of love, each with unique expressions and purposes, reflecting God’s divine plan for human relationships and personal growth through diverse emotional connections.
Eros: Romantic Love
Eros, often associated with romantic and passionate love, is a natural, God-given desire that reflects the intensity of human connection. Rooted in Greek philosophy, it emphasizes attraction, intimacy, and passion. While the Bible doesn’t explicitly use the term “eros,” it acknowledges romantic love through passages like the Song of Solomon, which celebrates the beauty of marital passion. Eros is a powerful force that, when balanced with self-control and commitment, enriches relationships. However, it can also lead to misuse if not guided by moral boundaries. The Bible encourages believers to view eros as a sacred gift, intended to flourish within the covenant of marriage. By aligning eros with divine principles, individuals can experience its fullness while honoring God’s design for love and relationships.

Storge: Familial Love
Storge refers to the natural affection and loyalty shared among family members, emphasizing bonds of kinship and shared experiences. While the Bible doesn’t explicitly use the term “storge,” it underscores the importance of familial love through various passages. For instance, the story of Joseph and his brothers illustrates deep familial ties despite conflicts. Storge is about nurturing and protecting one another, reflecting God’s design for family relationships. It highlights the responsibility to care for and prioritize one’s family, as seen in the command to “honor your father and mother” (Exodus 20:12). This type of love is foundational, teaching us to value and cherish our closest relationships. By fostering storge, we mirror God’s love and create a nurturing environment for personal growth and mutual support within families. It serves as a cornerstone for understanding deeper forms of love and connection in a biblical context.
Philia: Friendship Love
Philia, or friendship love, is rooted in mutual respect, trust, and shared experiences. The Bible emphasizes this bond through stories like David and Jonathan, who exemplified loyalty and deep affection. Philia goes beyond casual acquaintances, fostering a connection where individuals stand by one another through life’s challenges. It is about building strong, lasting relationships that often grow from shared values and faith. In Proverbs 27:17, it is noted that “iron sharpens iron,” highlighting how friends can inspire and strengthen each other. Philia encourages believers to nurture meaningful friendships that honor God and reflect His love. By investing in these relationships, we create a supportive community that uplifts and edifies one another. This type of love is a testament to the power of genuine connection and camaraderie, playing a vital role in our spiritual and emotional well-being.

Agape: Unconditional Love
Agape represents unconditional love, often described as selfless and divine. It is the highest form of love in the Bible, exemplified by God’s unwavering love for humanity. This love is not based on emotions or circumstances but is a deliberate choice to care for others without expectation of reward. Agape is central to Christian teachings, as seen in John 3:16, where God’s love for the world is demonstrated through the sacrifice of Jesus Christ. It transcends human limitations, emphasizing compassion, mercy, and forgiveness. Agape calls believers to love others extravagantly, mirroring God’s love for them. This type of love transforms lives, fostering a deep sense of connection and purpose. By embracing agape, individuals reflect God’s character, creating a ripple effect of kindness and grace in the world. It is the cornerstone of faith, guiding followers to love unconditionally, just as they have been loved.
Ludus: Playful Love
Ludus, or playful love, is characterized by joy, affection, and lightheartedness. It often manifests in the early stages of relationships, where there is excitement and mutual exploration. In the Bible, playful love is reflected in the joy of connection and the beauty of friendship. For instance, the friendship between David and Jonathan in 1 Samuel 18-20 embodies a deep bond that includes elements of ludus, as they shared laughter, trust, and mutual respect. Playful love also appears in the Song of Solomon, where the lovers express delight in each other’s company. Ludus is not merely romantic; it can also be seen in familial relationships, such as the playful interactions between parents and children. This type of love fosters a sense of togetherness and joy, reminding us that relationships should be enjoyed and cherished. It serves as a reminder to approach love with lightness and happiness, finding pleasure in shared moments.
Pragma: Enduring Love
Pragma represents enduring love, rooted in commitment, trust, and perseverance. It is the kind of love that stands the test of time and trials, demonstrating unwavering dedication. In the Bible, pragma is reflected in the covenantal relationships, such as marriage and faithfulness to God. For instance, the marriage of Isaac and Rebekah in Genesis 24 illustrates a commitment that endures through challenges and time. This type of love is not based on fleeting emotions but on deliberate choices to remain faithful and supportive. It is also seen in the biblical concept of perseverance, where believers are encouraged to endure trials with patience (James 1:2-4). Pragma teaches us that true love requires effort, loyalty, and a willingness to grow together through life’s ups and downs. It emphasizes the importance of building strong, lasting relationships grounded in trust and mutual respect.

Philautia: Self Love
Philautia refers to self-love, which is the appreciation and care for oneself in a healthy and balanced way. The Bible emphasizes the importance of self-respect and self-care, as seen in Jesus’ command to “love your neighbor as yourself” (Matthew 22:39). This type of love acknowledges that one cannot truly love others without first valuing oneself. It is not about self-worship or vanity but about recognizing one’s worth as a creation of God. Biblical self-love encourages believers to nurture their spiritual, emotional, and physical well-being, as they are temples of the Holy Spirit (1 Corinthians 6:19-20). By embracing philautia, individuals can cultivate a positive self-image, enabling them to love others more genuinely and serve God with a whole heart. This form of love fosters humility, self-awareness, and a deeper connection to faith and relationships. It is a foundation for living a life of purpose and integrity.
Understanding the seven types of love enriches relationships and fosters personal growth. Applying biblical love principles promotes a life of integrity, faith, and meaningful connections, reflecting God’s divine plan.
Personal and Relational Growth
Understanding the seven types of love fosters personal and relational growth by guiding individuals to embrace selflessness, empathy, and unconditional care. Agape love teaches self-sacrifice, while philia encourages deep, trusting friendships. Storge nurtures familial bonds, fostering loyalty and support. Eros, when aligned with biblical principles, promotes healthy intimacy. Ludus adds joy and playfulness to relationships, while pragma emphasizes commitment and endurance. Philautia highlights the importance of self-love, ensuring individuals can love others fully. By applying these principles, believers can build stronger, more meaningful connections, reflecting God’s character in their interactions. This growth not only enriches personal lives but also strengthens communities, demonstrating the transformative power of biblical love in everyday relationships and spiritual journeys.
Cultural Relevance and Faith
Biblical love remains universally relevant, transcending cultural boundaries and time. Its principles, rooted in faith, offer guidance for modern relationships and societal interactions. Agape, or unconditional love, exemplifies God’s character, calling believers to love others selflessly, regardless of cultural differences. This love fosters unity and compassion, bridging divides in a diverse world. Faith plays a central role, as trusting God’s plan and submitting to His will enables individuals to demonstrate love authentically. Prayer and seeking God’s wisdom are essential in navigating cultural complexities, ensuring that love is expressed in ways that honor Him. By embracing these teachings, believers can impact their communities, reflecting God’s love in a way that resonates across cultures and generations, making biblical love a timeless and transformative force in society.

